Applications
Water and waste management is important. The major goal of wastewater treatment is to remove solids from raw sewage before the remaining water, called effluent, is discharged back into the environment. If wastewater is not properly treated, the environment and human health can be negatively impacted. As solid material decays, it uses up oxygen, which is needed by the plants and animals living in the water.
The wastewater treatment plant uses rubber expansion joints on all the piping systems as well as slurry and sludge pumps. Expansion joints are mainly used to eliminate vibration within the piping system and to account for piping misalignment. The odor control side of the waste water treatment plant uses flue duct expansion joints on the FRP ducting systems.
Some wastewater streams cannot be treated biologically because they are not biodegradable. In these instances wastewater plants use high temperature incinerations systems to dispose of the remaining solids. The incineration units utilize high temperature composite expansion joints. In addition to the incineration unit, expansion joints are used downstream on the environmental control systems.
Water and Waste Management Applications
- Waste Water Collection Systems
- Wet Wells Sewer Pump Inlet
- Wet Wells Sewer Pump Outlet
- Overflow piping
- Preliminary Treatment Pump Inlet
- Preliminary Treatment Pump Outlet
- Gravity Controlled Grit Removal
- Blower Outlet
- Odor Control Fan Inlet
- Odor Control Fan Outlet
- Secondary Treatment Aeration System Piping
- Digester Pump Inlet
- Digester Pump Outlet
- Digester Roof Expansion Joint
- Incinerator Outlet
- Heat Recovery Steam Duct
- Electrostatic Precipitator Gas Inlet
- Electrostatic Precipitator Gas Outlet
- ID Fan Gas Inlet
- ID Fan Gas Outlet
- Stack Inlet
Waste Water irrigation
Rubber expansion joints are often used on waste water irrigation pipelines because they are much more forgiving compared to metal expansion joints.
Design Considerations

- If expansion joints are installed underground the use of a metal shroud is recommended.
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: 50F
- Media: Water
- Particulate: Minimal
- Operation: Often these pipelines are underground
- Pressure: 120 to 150 PSI
- Movements: Moderate
- Expansion joint Recommendation: Holz 320EZ style should be used
Wet wells are the holding area for gravity flow sewer systems. As sewage enters the wet well and the water level rises, pumps are engaged to pump out the sewage to a forced main, or the sewage is lifted to a higher grade to continue the gravity flow to the outlet point.
Design Considerations
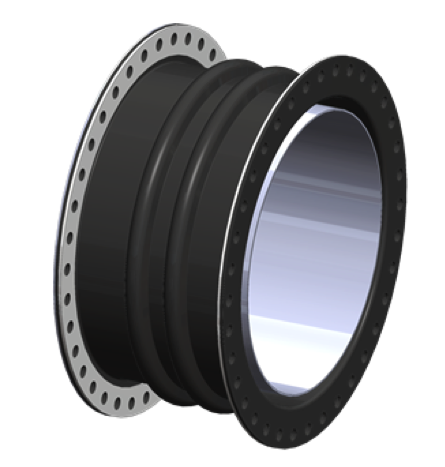

- Filled arch is recommended due to heavy particulate environment to prevent build up in the arch area.
- Flow liner recommended
- Extra thick tube is recommended due to abrasive environment
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: 70 to 180F
- Media: Sewage
- Particulate: Heavy
- Operation:
- Pressure: 25” HG
- Movements: Moderate
- Expansion joint Recommendation: Holz Style 320FA-2 should be used
Wet wells are the holding area for gravity flow sewer systems. As sewage enters the wet well and the water level rises, pumps are engaged to pump out the sewage to a forced main, or the sewage is lifted to a higher grade to continue the gravity flow to the outlet point.
Design Considerations

- Filled arch is recommended due to heavy particulate environment to prevent build up in the arch area.
- Flow liner recommended
- Extra thick tube is recommended due to abrasive environment
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: 70 to 180F
- Media: Sewage
- Particulate: Heavy
- Operation:
- Pressure: 80PSI
- Movements: Moderate
- Expansion joint Recommendation: Holz Style 320FA-2 should be used
Overflow piping is used for storm water run off
Expansion joint Specifications

- Temperature: Ambient
- Media: storm water
- Particulate: minimal
- Pressure: 1 to 3 PSI
- Movements: minimal
- Expansion joint Recommendation: Holz 940 or 942 style should be used
Design Considerations
- Piping is typically non-standard so a custom size expansion joint is required.
The initial stage in the wastewater treatment process is preliminary treatment. The purpose of preliminary treatment is to protect the plant equipment by removing solid materials which can cause clogs, jams, or excessive wear to plant machinery. The main preliminary treatment process is screening, which consists of removing large solids such as rags, cans, rocks, branches, or leaves from the flow before moving on to downstream processes. Expansion joints are used on the pumps which transport the screened wastewater to the grit removal systems.
Design Considerations

- Filled arch is recommended due to heavy particulate to prevent build up in the arch area.
- Flow liner recommended
- Extra thick tube is recommended due to abrasive environment
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: 70 to 180F
- Media: Sewage
- Particulate: Heavy
- Operation:
- Pressure: 25″ HG
- Movements: Moderate
- Expansion joint Recommendation: Holz Style 320FA-2 should be used
Design Considerations

- Filled arch is recommended due to heavy particulate environment to prevent build up in the arch area.
- Flow liner recommended
- Extra thick tube is recommended due to abrasive environment
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: 70 to 180F
- Media: Sewage
- Particulate: Heavy
- Operation:
- Pressure: 80PSI
- Movements: Moderate
- Expansion joint Recommendation: Holz Style 320FA-2 should be used
The purpose of grit removal is to remove the heavy inorganic solids that could cause excessive mechanical wear. Grit includes sand, gravel, clay, egg shells, coffee grounds, and seeds. Several processes and devices are used for grit removal. Processes include gravity, aeration, chemical addition, or centrifugal force to separate the solids from the wastewater.
Design Considerations
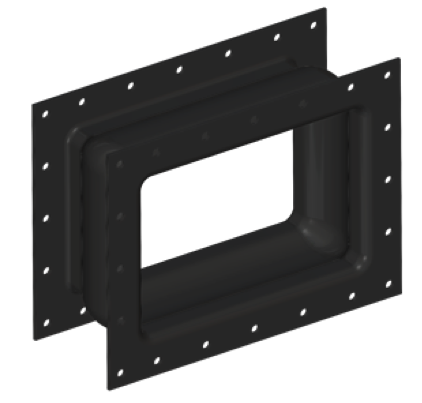
- Flow liner recommended due to heavy particulate
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: Ambient, 35F to 110F
- Media: inorganic solids
- Particulate: Heavy
- Operation: Gravity feed chute
- Pressure: 0 to 1 PSI
- Movements: Minimal
- Expansion joint Recommendation: Holz fully molded 945 Style
The purpose of the blower is to keep the lighter organic solids in suspension while allowing the heavier grit particles to settle out. This is achieved by creating additional air flow in the water treatment system. Proper air supply is critical to various functions such as keeping bacteria suspended, aiding in flocculation, and supplying sufficient oxygen transfer for BOD removal and nitrification.
Design Considerations
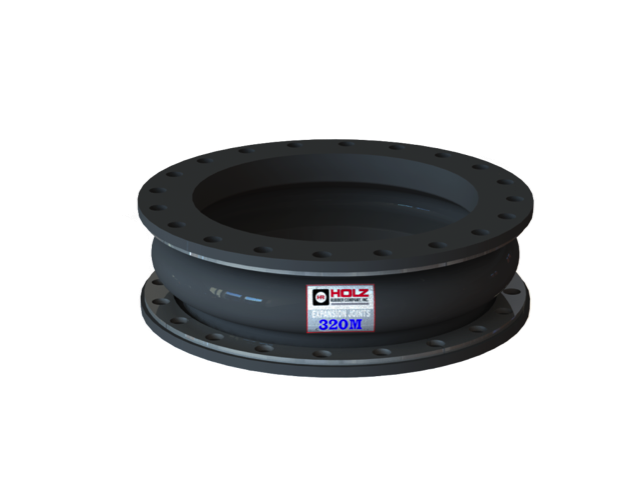

- Often plant operators set pressure points too high and excess blower discharge pressure occurs. It is important to consider excursion pressures.
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: 70 to 160F
- Media: air
- Particulate: minimal
- Pressure: 80 to 200PSI
- Movements: Moderate
- Expansion joint Recommendation: Holz 320M style or 981 floating flange should be used
Once the grit has been removed from the waste water it enters a primary clarification tank or basin. In the clarification tank the solids heavier than water settle to the bottom while solids lighter than water float to the top. The settled solids are removed as scum and the wastewater leaves the tank to the next stage of treatment. The treatment of this wastewater results in a variety of unwanted hazardous gases, such as Hydrogen Sulfide and Sulfur Dioxide. Fans are used to move these gases and fumes to pollution control system or other devices.
Design Considerations

- Mating flanges are typically FRP so reactive forces must be considered.
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: 180 to 220F
- Media: Sulphide gases
- Particulate: minimal
- Pressure: slightly negative, 1 to 2 PSI
- Movements: Minimal, mostly vibration
- Expansion joint Recommendation: Holz fully molded 945 style
Design Considerations

- Mating flanges are typically FRP so reactive forces must be considered.
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: 180 to 220F
- Media: Sulphide gases
- Particulate: minimal
- Pressure: slightly positive, 1 to 2 PSI
- Movements: Minimal, mostly vibration
- Expansion joint Recommendation: Holz fully molded 945 style
The main purpose of secondary treatment is to provide biochemical oxygen demand removal beyond what is achievable by primary treatment. Secondary treatment refers to those treatment processes that use biological processes to convert dissolved, suspended, and colloidal organic wastes to more stable solids that can be either removed by settling or discharged to the environment without causing harm.
Most secondary treatment processes decompose solids aerobically producing carbon dioxide, stable solids, and more organisms. Because solids are produced, all of the biological processes must include some form of solids removal.
Aeration is commonly used to treat water that contains trapped gases that can impart an unpleasant taste and odor to the water. Just allowing the water to rest in a vented tank will drive off much of the gas, bus usually some form of forced aeration is needed. Expansion joints are utilized on the aeration system piping.
Design Considerations

- Depending on system configuration double arch expansion joints are often utilized.
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: 70 to 160F
- Media: Air
- Particulate: Minimal
- Pressure: 80 to 160PSI
- Movements: Moderate
- Expansion joint Recommendation: Holz 320 style or 320-2 style should be used
The wastewater in the secondary treatment is full of living microorganism and activated sludge. The activated sludge is constantly growing, and more is produced than can be returned for use in the aeration basin. Some of this sludge must be transferred to sludge handling systems for treatment and disposal. The digester pumps are used to transfer sludge to the digester. Digesters are used to stabilize the solids that are removed from the waste water treatment.
Design Considerations
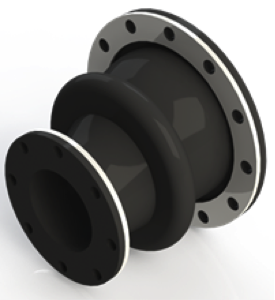
- The use of tapered expansion joints on digester pumps is common.
- Filled arch should be utilized to prevent arch caking
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: 70 to 120F
- Media: sludge
- Particulate: Moderate
- Pressure: 24″ HG
- Movements: Vibration to minimal movement
- Expansion joint Recommendation: Holz Series 320FA should be used
Design Considerations

- The use of tapered expansion joints on digester pumps is common.
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: 70 to 120F
- Media: sludge
- Particulate: Moderate
- Pressure: 100PSI
- Movements: Vibration to minimal movement
- Expansion joint Recommendation: Holz 320FA style should be used
The digester roof expansion joints purpose is to contain the hydrogen sulfide gas in the digester.
Design Considerations

- Hydrogen sulfide gas content can be extreme in this application, as high as 1200ppm while average is 850ppm
- Typically 100′ diameter concrete tanks. The fixed roof is cut in quarters leaving 4 expansion joints that run from the outside perimeter to the center of the tank.
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: 85 to 100F
- Media: anaerobic digester/wastewater – hydrogen sulfide
- Particulate: Moderate
- Pressure: 25″ Water Column
- Movements: up to 1″
- Expansion joint Recommendation: Teflon or Butyl, belt style
Some wastewater streams cannot be treated biologically because they are not biodegradable, take a long time to biodegrade or contain substances that are toxic to bacteria. The waste water treatment plants then use high temperature incineration systems to remove the solids in the digester.
Design Considerations
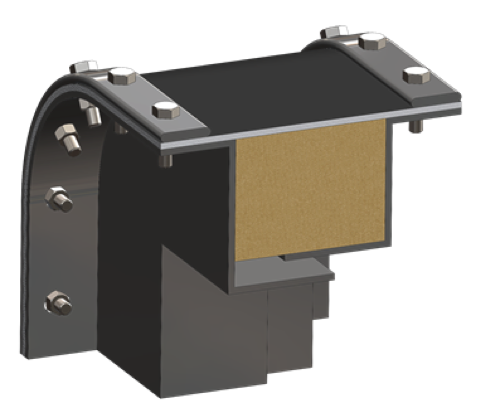
- Composite design and pillow recommended to eliminate the possibility of mechanical damage due to flutter
- Since temperatures are well above flue gas dew point during continuous system operation, the system will be dry and chemical barriers are not necessary
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: 600 to 850F
- Media: Flue gas from waste combustion in incinerator
- Particulate: Heavy particulate
- Pressure: 40 to 50″ Water Column
- Movements: Large lateral and compression expected
- Expansion joint Recommendation: High temperature expansion joint – Holz Series 1000HTF should be used
The hot flue gas leaving the incinerator is recycled to be used as process steam. Expansion joints are used on the heat recovery ducting.
Design Considerations

- Metal joints are often replaced in this application due to vibration fatigue
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: 250F
- Media: Steam
- Particulate: Minimal
- Operation: Vibration fatigue is common
- Pressure: 30″ Water Column
- Movements: Depending on system configuration excessive vibration or moderate movements
- Expansion joint Recommendation: Holz fully molded 952 style should be used
An Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP) is a large industrial emission control unit that uses a fabric expansion joint on both the inlet and outlet. The ESP traps and removes fine dust and aerosols from the exhaust gas stream by using an electrostatic charge.
Design Considerations
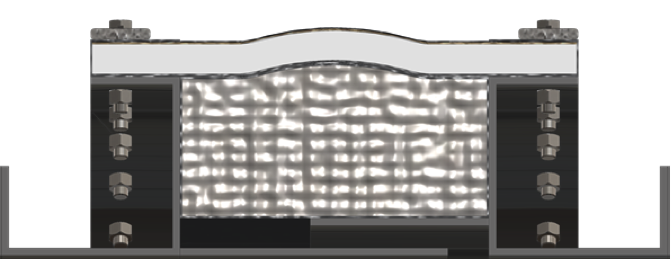
- A composite should be used
- Flow liner is required, if breach opening exceeds 12″ a double overlapping flow liner should be used
- Use of a pillow will inhibit direct impingement of the particulate that will be present
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: 600F to 800F,
- Media: Hot flue gas
- Particulate: moderate
- Operation: Long duration between outages, typically 18 months
- Pressure: Positive 40″ to 50″ Water Column
- Movements: Large lateral and compressive movements due to high temperature
- Insulation/Lagging: Do not lag over expansion joint. Remove lagging from flanges to allow radiant cooling
- Expansion joint Recommendation: High temperature expansion joint – Holz Series 1000HTF or 800HTF should be used
Design Considerations

- Must consider the possibility of dew point (wet condition). A PTFE gas barrier can be added for increased chemical resistance
- Flow liner required when using a PTFE product
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: 350F to 500F, Excursions to 600F
- Media: Flue gas from precipitator
- Particulate: Minimal
- Operation: Dew point could present potential corrosion problems
- Pressure: Ranges from slightly negative to slightly positive, -5″ to +5″ water column
- Movements: Moderate compressive and lateral movements expected
- Insulation/Lagging: Temperatures allow lagging
- Expansion joint Recommendation: High temperature expansion joint – Holz Series 600HTF or PTFE should be used
An Induced Draft Fan is located after the Electrostatic Precipitator. It pulls the flue gas through the ductwork and out of the stack into the atmosphere. Expansion joints are used on the inlet and outlet of the ID fan to absorb vibration.
Design Considerations
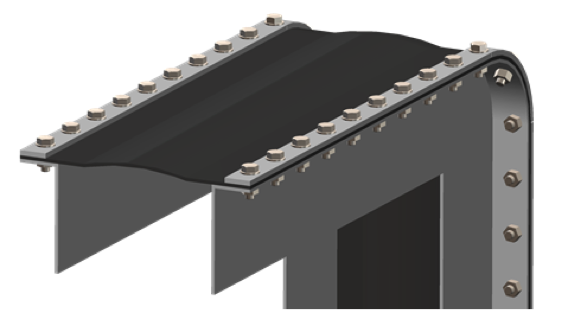
- Many induced draft fans utilize small dual inlets with control or shutoff dampers. Designs must not interfere with damper blades
- Flow liner is required when using a composite
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: 300F to 500F
- Media: Flue gas from Precipitator
- Particulate: Minimal
- Operation: Although movements are not severe temperatures will approach dew point and present potential corrosion problems
- Pressure: Slightly negative, -15″ water column
- Movements: Minimal movement, primarily vibration
- Expansion joint Recommendation: Depending on conditions a E14GGN, V14GGN, or 600HTF can be used
Design Considerations

- Many induced draft fans utilize small dual inlets with control or shutoff dampers. Designs must not interfere with damper blades
- Flow liner is required when using a composite
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: 300F to 500F
- Media: Flue gas from Precipitator
- Particulate: Minimal
- Operation: Although movements are not severe temperatures will approach dew point and present potential corrosion problems
- Pressure: Slightly negative, -15″ water column
- Movements: Minimal movement, primarily vibration
- Expansion joint Recommendation: Depending on conditions a E14GGN, V14GGN, or 600HTF can be used
The stack releases the flue gas into the atmosphere
Design Considerations
- Many induced draft fans utilize small dual inlets with control or shutoff dampers. Designs must not interfere with damper blades
- Flow liner is required when using a composite
Expansion joint Specifications
- Temperature: 120 to 180F
- Media: Clean Flue Gas
- Particulate: Negligible
- Operation: Although movements are not severe temperatures will approach dew point and present potential corrosion problems
- Pressure: Slightly positive to slightly negative, 15″ water column
- Movements: Moderate movement
- Expansion joint Recommendation: Depending on conditions a E14GGN, V14GGN, or 600HTF can be used